What is a liquid cooling loop?
Liquid cooling loops or chiller loops circulate cooling fluids to a process to keep it at a desired temperature. These loops are used in a variety of different industries, from semiconductor manufacturing, to brewing and fermentation chambers, to hydrogen fuel cells. In many processes, such as thermal testing of semiconductor components like processors, very precise control of the coolant loop is required within a fraction of a degree.
In order to precisely control the temperature in that cooling loop, the flow and pressure of the cooling liquid through the loop needs to be accurately controlled. Most commonly, this is accomplished by putting a back pressure regulator or pressure sustaining valve in a recirculation loop with a pump.
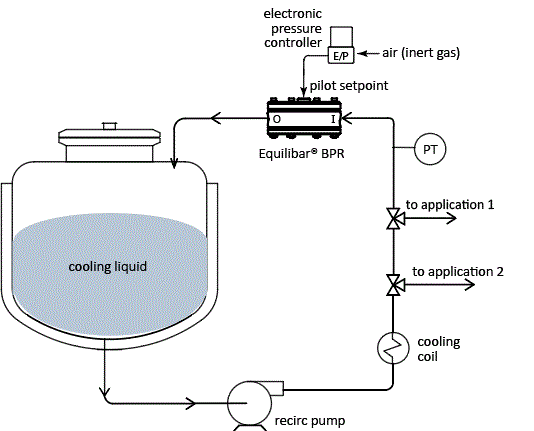
Equilibar BPR is used to control a liquid cooling loop for precise temperature control to various applications
Commonly, one cooling loop like this may feed multiple machines within a plant, with the amount of liquid being recirculated back to the holding tank varying depending on the number of machines online at any given moment. Compared to traditional spring-loaded valves and control valves, Equilibar back pressure regulators (BPRs) have a wide Cv range and turndown of 100:1 or more, allowing for stable control of the pressure in the cooling loop as that recirculated flow varies. Additionally, Equilibar BPRs can be easily automated with an electronic pilot regulator controlling the reference air pressure on the dome of the BPR. The multi-orifice design of Equilibar valves also prevents cavitation damage that is a common concern for single seat valves in high dP liquid systems.

Equilibar back pressure regulator with electronic pilot control for easy automation
Using Equilibar Valves for Temperature, Level, pH and other Parameters Related to Flow
Equilibar valves can also be used as a control valve to directly control the flow or temperature in a cooling loop. When set up in a PID control loop with a flow meter and an electronic pilot pressure regulator, an Equilibar valve works extremely well to control precise flow.
An article published in the November 2020 edition of Flow Control Magazine shares how Equilibar valves can be used to directly control flow or use pressure and flow control schemes to regulate other parameters such as level, pH, coating weight and temperature. The benefit of the Equilibar’s wide Cv range holds for setups like this as well, allowing for precise control across a wide range of operating conditions.
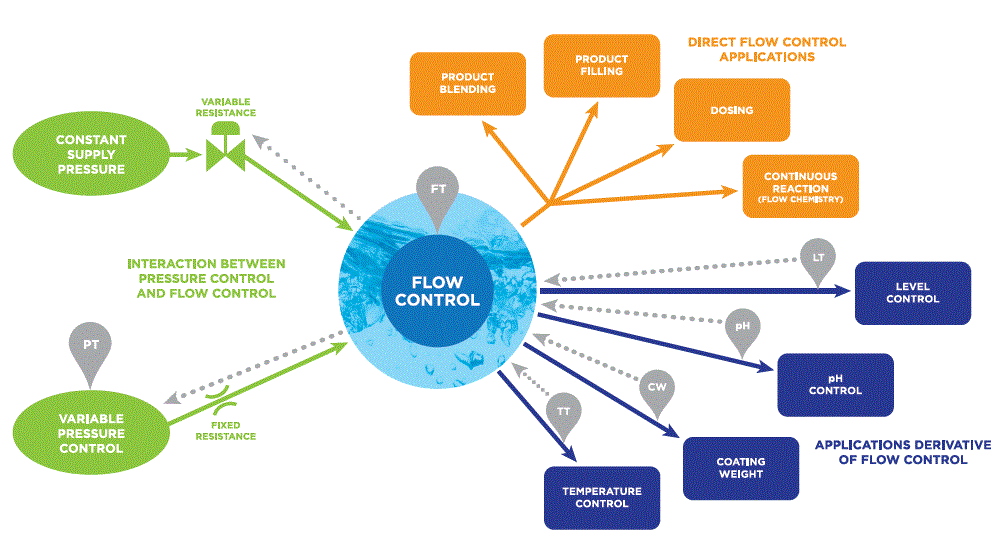
Equilibar valves are used in process control setups to control flow and other variables derivative of flow control
In addition to this greater precision, the simple construction of the Equilibar valves allows for quick maintenance with most valves being able to be rebuilt as new in the field within a matter of minutes. This simple design also allows for more customization options in body, diaphragm, and O-ring materials for corrosive fluids or aggressive temperatures.
Get More Information


